Scientific Support
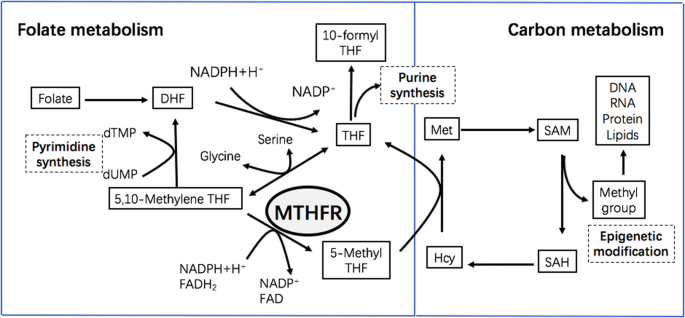
The scientific literature supports the involvement of iodide, selenium, and molybdenum as essential to activation of vitamin B2. Vitamin B2 in the active form of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is the co-enzymatic form that allows MTHFR to function, hence is involved in methylation. Here are several papers that explain the interconnected dynamic of iodide, selenium, molybdenum, vitamin B2, and folate in vitamin B12 activation.
[This paper explains how both iodine and selenium are involved in thyroid hormone production.]
Schomburg, L. and Köhrle, J. (2008), On the importance of selenium and iodine metabolism for thyroid hormone biosynthesis and human health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 52: 1235-1246. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700465
"It had been shown that thyroxine regulates the conversion of riboflavin to riboflavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) in laboratory animals. In the hypothyroid rat, the flavin adenine dinucleotide level of the liver decreases to levels observed in riboflavin deficiency. We have shown that in six hypothyroid human adults, the activity of erythrocyte glutathione reductase, an accessible FAD-containing enzyme, is decreased to levels observed during riboflavin deficiency. Thyroxine therapy resulted in normal levels of this enzyme while the subjects were on a controlled dietary regimen. This demonstrates that thyroid hormone regulates the enzymatic conversion of riboflavin to its active coenzyme forms in the human adult."
"In the entire studied population, the concentration of vitamin B2 was significantly negatively correlated with TSH level (R = − 0.254; p < 0.005). In the control group, there was a positive correlation between vitamin B2 concentration and fT4 level (R = 0.378; p < 0.005). Moreover, in the [Hashimoto's] group, there was a negative correlation between vitamin B2 concentration and TSH level (R = − 0.250; p < 0.005) and positive with age (R = 0.262; p < 0.005)." [This is saying that people with reduced thyroid output were shown to have lower vitamin B2 status.]
Mikulska-Sauermann, A.A., Karaźniewicz-Łada, M., Filipowicz, D. et al. Measurement of Serum Vitamins B2 and B6 in Patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis by LC–MS/MS Method. Chromatographia 87, 433–443 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-024-04319-x
"Activation of riboflavin into its physiologically important coenzymes requires an initial phosphorylation by flavokinase (ATP:riboflavin 5-phosphotransferase) to form FMN and a subsequent pyrophosphorylation with AMP catalyzed by FAD synthetase (ATP:FMN adenylyl transferase). Both flavin biosynthetic enzymes are up-regulated by thyroid hormones in most mammalian cells."
"Primary deficiencies and diminished intestinal transport are not the only causes of riboflavin deficiency. Endocrine abnormalities (aldosterone and thyroid hormone insufficiency), specific drugs (tricyclic antidepressants and tetracyclic antibiotics), and ethanol abuse may interfere significantly with riboflavin utilization."
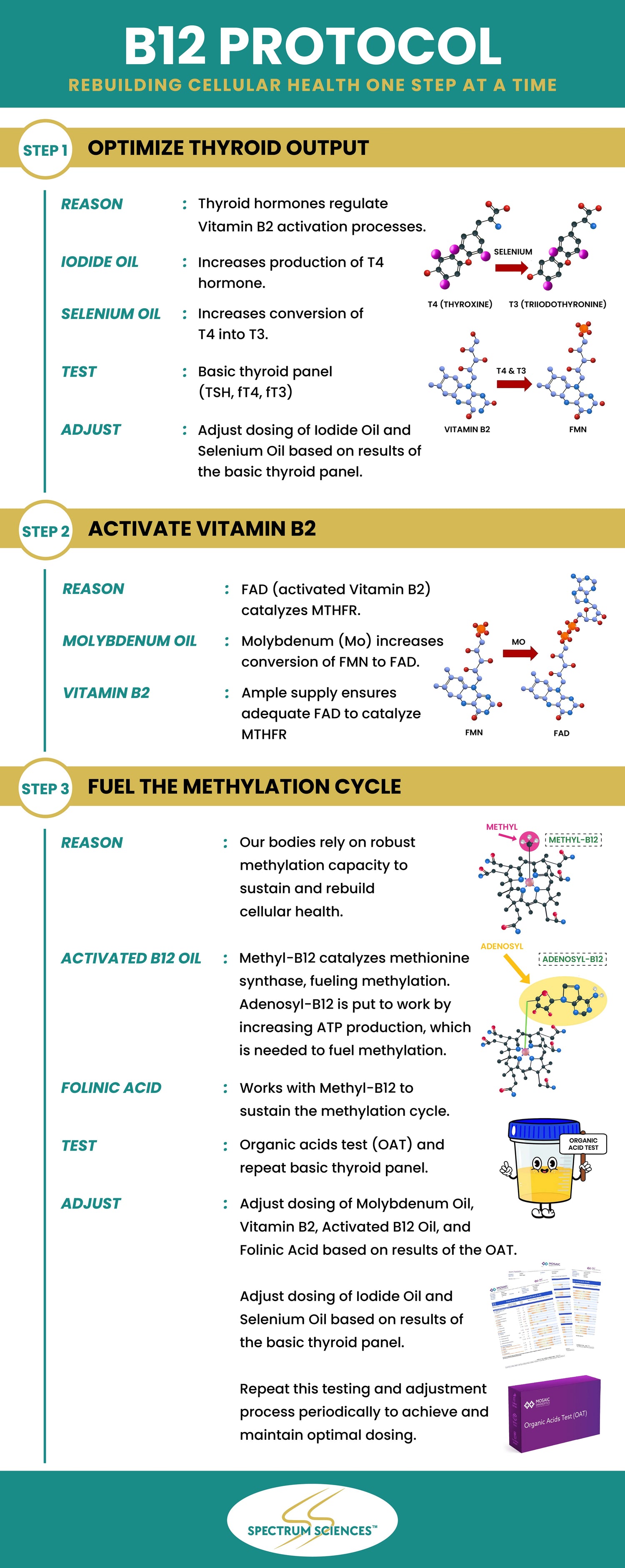
Scientific framework for The B12 Protocol can be found in these supporting literature references.